Intro
The Certified Kubernetes Administrator (CKA) exam is one of the most recognized Kubernetes certifications, proving your ability to manage, troubleshoot, and configure K8s clusters. But unlike traditional exams, CKA is 100% hands-on—no multiple-choice, just real-world challenges.
In this post, I’ll break down:
✅ Exam structure & key domains
✅ How I prepared (resources, labs, and time investment)
✅ Tips to ace it on your first attempt(or 2nd 😁)
The exam summary
All key details about the exam and objectives can be found on the official CNCF page. However, here are the most important points :
Length: 2 hours.
Questions: Around 15–20 hands-on tasks (no multiple choice).
Exam format: Lab based (you’ll be working in a live Kubernetes environment).
Recommended exp: 6–12 months of hands-on Kubernetes experience, but strong lab practice can compensate.
Pass Score: 66% (out of 100%).
Score per topic: Provided in the exam report.
Exam center: Online, proctored via PSI ( previously Examity).
Retake Policy: One free retake included if you fail.
Pass confirmation: Instantaneous.
FREE Exam simulations: Two trial sessions on killer.sh
Validity: 2 years.
Price: $395 (old price) but you can get 50% discounts (especially during holidays)
Preparation time:
With a prior K8s exposure, I spent almost ~2 months—20 days on the course (plus notes)+ 10 days on exam labs—and practiced 150+ scenarios for solid hands-on prep.
Impressions
What Sets CKA Apart for me ?
✅ 100% hands-on—no MCQs fluff ! You will really feel that you acquired a lasting knowledge after the exam.
✅ Real-world skills—It’s all about learning by doing, not memorizing like a parrot.
✅ Teaches you to deploy anything using K8s docs at lightning speed, you’ll forget Google exists. 😉
Was It Tough?
Absolutely! I failed once, but bounced back two days later and passed. ⏱️Beating the clock is key, so It’s not much the knowledge but how fast can you execute without loosing your calm when something goes wrong.
Exam guide
The CKA exam guide is available on the Linux Foundation certification page, and you’ll find various versions online.
- The best starting point is the official CKA Curriculum along with the Candidate Handbook and the Exam Tips .
CKA Curriculum
| Curriculum Section | Details |
|---|---|
| 10% – Storage |
|
| 30% – Troubleshooting |
|
| 15% – Workloads and Scheduling |
|
| 25% – Cluster Architecture, Installation and Configuration |
|
| 20% – Servicing and Networking |
|
Our ultimate bundle notes (Coming soon)
I took extra time to prepare because I created detailed flashcards covering key concepts and tips. Even for a hands-on exam, having quick references helps. Stay tuned—I’ll share them soon on the CloudThrill blog! 🚀
Resources to Pass the CKA
Like many, I searched for the best training materials online. While I couldn’t take multiple courses due to the time commitment, I used a course available at AcloudGuru subscription
I. Courses
ACloudGuru CKA Course
This required a subscription for which I thank Cloudthrill for providing.
- Pros
- Top-notch platform for cert prep with 100s of labs.
- Great balance of theory and hands-on learning.
- Includes 10x exam practice tests covering key sections.
- Cons
- 24+ hours of theory, more if you take notes.
- Labs run an older K8s version than the actual exam.
- Pro Tip Stay consistent—avoid long breaks between chapters!
KodeKloud CKA Certification Course
- Pros
- Ideal for Absolute beginners with 320 Lessons in 25 Hours
- 17 Modules , 70 Labs,
- Mock exam
- Discord Community support
- Cons
- I had a free 6-month subscription, but flagship certifications aren’t included, which feels a bit misleading.
II. Other resources
- Kubernetes Docs – Your go-to reference for everything K8s.
- Kubernetes blogs – handy to explore new release features demos.
- GitHub CKA Exercises – A collection of practice exercises with solutions ( see also crash-course & ckad-prep) .
- CKA Doc bookmark: A web bookmark to help you navigate K8s documentation while resolving labs.
- Official Kubernetes Cheat sheet
CKA Simulators
Practice labs in a real Kubernetes environment are so vital to ace the exam and build confidence in this hand-on challenge. You need to train your brain to be surgical in doc searches and act fast. Whether you prefer deploying manifests or mastering kubectl, simulators are a must.
🏆 Killer.sh (included)
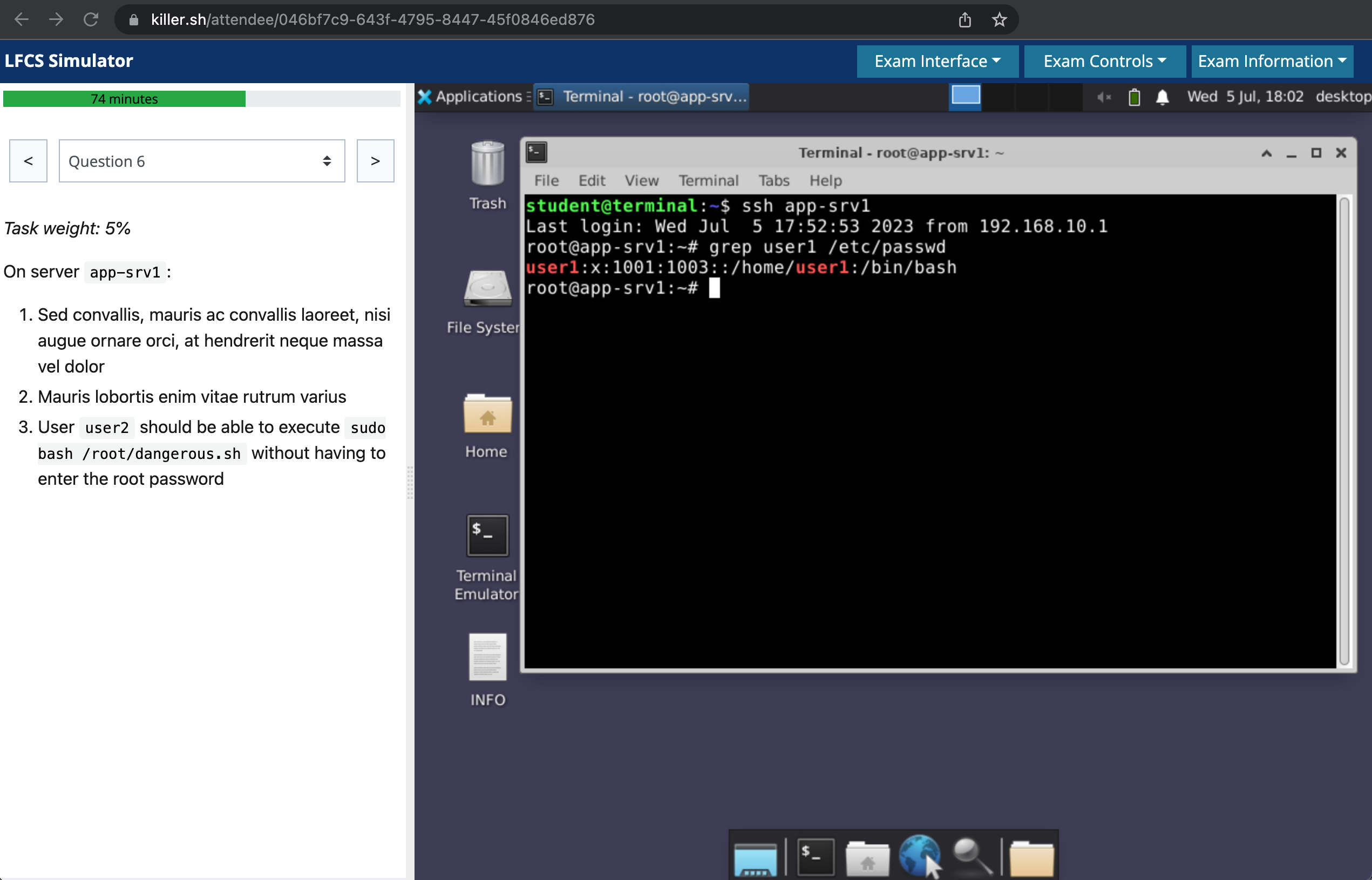
- Killer.sh Provides the exact exam environment and experience.
- CKA candidates get 2 free attempts after registration.
- Includes 17 scenarios that are harder than the exam’s including their solutions.
- Each simulator session runs most resent K8s version (i.e 1.31) and is open for 36 hours.
- You can continue answering questions even after the exam mode clock runs out (score keeps being updated).
🚀 KillerKoda (free)
Killercoda is another playground for linux or K8s environments built by killer.sh creator(Kim Wüstkamp).This is by far my favorite platform.
- Offers interactive, browser-based Kubernetes scenarios (for cka, cks, ckad and many more).
- You can create your own scenarios and share with others by using the creator feature .
- super useful for exploring broader use cases.
I completed 130+ scenarios—and my favs are:
- Kim Wüstkamp [20+ scenarios] solutions are included
- Sachin H R [74 scnearios] , solutions are available in pdf here
🔥 Iximiuz
Iximiuz (excellence) is an Indie Learning Platform to Master Server Side Craft created by Ivan Velichko with sandboxes and playground using Microvms.
The platform has a full section for Kubernetes chalenges including CKA.
Exam Tips
1. Get your things together
- Don’t loose your cool if something doesn’t work try the next task and don’t get stuck for more than 10 minutes.
2. General Exam Strategy
- Prioritize Easy Questions : Start with smaller, simpler tasks to build confidence. Skip multi-paragraph questions initially; come back later.
- Aim for Partial Credit: Even if you can’t fully solve a problem, submit what you have—every bit helps.
- Read Carefully: Read questions twice to ensure you understand the requirements before acting.
3. Resource & Backup Tips
- Backup Before Edits: Export resources (e.g.,
kubectl get ... -o yaml > backup.yaml) before edits or deletions. - Node Draining: Save manifests before draining a node so you can recreate Pods if needed.
- Imperative Commands: Use
kubectl create/runfor quick resource creation. Check parameters via-h.
Export do="--dry-run=client -o yaml"
# deployments
k create deploy web-deployment --image=nginx $do > deployment.yam
k scale deploy <name> --replicas=4
kubectl set image deployment my-deploy <name of container>=<new image name>
# pods
kubectl run fast-nginx --image=nginx nginx -- /bin/sh -c 'sleep 3600' -n dev $do > mypod.yml
kubectl run tmp-shell --rm -i --tty --image nicolaka/netshoot -- /bin/bash
# other
kubectl create service..
kubectl create ingress world --class=nginx --rule="example.com/europe/=europe:80" \
--rule="world.universe.mine/asia/=asia:80" -n world
k expose deploy my-dep --port 80 -n demo-ns
# roles
kubectl create serviceaccount my-service-account --namespace default
kubectl create role my-role --namespace default --verb=get --verb=list --verb=watch --resource=pods
kubectl create rolebinding my-role-binding --namespace default --role=my-role --serviceaccount=default:my-SA
4. Context & CLI
- Use Aliases & Shortcuts: For example,
export do="--dry-run=client -o yaml"to speed up operations. - Check Your Context: run
use-contextcommand at the top, so you always know which cluster you’re working on. - Master json Outputs: use the sheet cheat to learn filtering fields from json output and patching a resource.
# Produce a period-delimited tree of all keys returned for nodes
# Helpful when locating a key within a complex nested JSON structure
kubectl get nodes -o json | jq -c 'paths|join(".")'
kubectl get pods -n kube-system -o json | jq -r '.items[] | select(.metadata.name | startswith("coredns")) | .metadata.name'Patching resources
# Partially update a node
kubectl patch node k8s-node-1 -p '{"spec":{"unschedulable":true}}'
# Update a container's image; spec.containers[*].name is required because it's a merge key
kubectl patch pod valid-pod -p '{"spec":{"containers":[{"name":"kubernetes-serve-hostname","image":"new image"}]}}'
# Update a container's image using a json patch with positional arrays
kubectl patch pod valid-pod --type='json' -p='[{"op": "replace", "path": "/spec/containers/0/image", "value":"new image"}]'
# Disable a deployment livenessProbe using a json patch with positional arrays
kubectl patch deployment valid-deployment --type json -p='[{"op": "remove", "path": "/spec/template/spec/containers/0/livenessProbe"}]'
# Add a new element to a positional array
kubectl patch sa default --type='json' -p='[{"op": "add", "path": "/secrets/1", "value": {"name": "whatever" } }]'
# Update a deployment's replica count by patching its scale subresource
kubectl patch deployment nginx-deployment --subresource='scale' --t5. Exam Environment & Technicals
- Root Access: Run
sudo -ias needed. Do not reboot the base node. - No Blocking Ports: Leave
8080/tcp,4505/tcp, and4506/tcpopen. Don’t tamper with thecerterminalprocess. - Keyboard Shortcuts:
- Inside terminal: Copy =
Ctrl+Shift+C, Paste =Ctrl+Shift+V. - Use
Ctrl+Alt+Winstead ofCtrl+Wto avoid closing tabs.
- Inside terminal: Copy =
- SSH & Cluster Nodes: You can SSH into each node; remember to return to the base node (
node-1) after each task. - Disable extra Keyboard languages: This caused a chaos as I couldn’t switch back through the remote full screen.
VIM vs YAML
- Copy & Paste:
Esc + V(visual mode) → highlight text →y (yank) or d (cut)→move cursor→p or Pto paste. - Line Numbers:
:set nu. Jump to a line::22. - Indent Multiple Lines:
Esc + V, highlight lines, then press>or<(repeat with.).
Conclusion – Certified now what?
Although the exam tests hands-on skills, it doesn’t fully prepare you for the depth of real-world SRE scenarios.
Further learning ?
We suggest you to focus on advanced Kubernetes use cases and operators for networking, security, and storage. Recommended areas include:
- cert-manager, Ingress, External DNS, Gateway API
- Load Balancers, Service Mesh (Linkerd, Cilium, Istio)
- GitOps (Flux, Argo CD), Helm Charts
- Security (Kuebscape, Trivy, External-Secrets, external KMS, Vault)
- Storage (CSI for file systems)
- Building Proof-of-Concept applications on managed clusters (EKS, GCP, AKS, OKE).
Good luck!