Introduction:
This document provides a step-by-step deployment procedure with some of best practices to install and configure an Oracle Real Application Clusters (RAC) Database 12c Release 1 (12.1)* with Oracle ASM on Linux RedHat Entreprise 7 virtual machines (Virtualbox). Most of it is inspired by the RACAttack project that was written collaboratively by many authors all around the world (Seth Miller, Yury Velikanov, Ludovico Caldara and Björn Rost…to name a few) .
If you want to learn more or contribute to the project please visit their official Wiki Page.
In addition I have inserted some relevent guidelines regarding Oracle 12c on RHEL 7 from RedHat’s website (Deploying Oracle RAC Database 12c on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 – Best Practices)
Implementation process:
We will focus on the following tasks:
Main steps
1. Setup VirtualBOX
– Configuring Device Mapper Multipathing
– Using udev Rules instead of Oracle ASMLib
5. Install Grid Infrastructure 12c Release 1
6. Install Database Software 12c Release 1
Lab environment requirement & overview
Host requirement:
a. Hardware:
RAM : min 8 GB – actual 10 GB
DISK: min 50 GB – actual 500 GB
Internet connection
b. Software:
Host: OS – Windows /Linux Hypervisor – virtualBox Other tools needed: Putty, Vnc Viewer
Guest: OS – Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.1 (x86_64) or the Centos 7 equivalent .
* RedHat free Evaluation Subscription can be done by creating an account with a business email address (here).
Oracle software –
1- Login to: http://edelivery.oracle.com/ with your Oracle Account
2- On the Media Pack Search page, select:
Product pack: Oracle Database Platform: Linux x86-64
3- Click GO then Select and download the following products :
Grid Infrastructure 12c Release 1 (12.1.0.2.0) and Oracle Database 12c Release 1 (12.1.0.2.0)
|
Disk space consumed for Oracle Grid Infrastructure Home and Oracle Database Home Enterprise Edition may vary.
Swap Space (Recommended) :
Filesystem layout to properly install the Oracle Grid Infrastructure and Oracle Database software
|
1. Setup VirtualBOX Go to Top
a. Network configuration : I have used the following network setup. Feel free to adjust to your needs:
– Hostnames london1,london2 Domaine: Evilcorp.com ( Mr Robot fan here…)
– Public IPs 192.168.78.0/24 (51,52)
– Interconnect 172.16.100.0/24 (51,52)
o Private IPs available from RAC nodes only
– SCAN
o Name => london-cluster-scan.evilcorp.com
o IPs => 192.168.78.251/252/253
b. Preparation:
1. From the main VBOX screen, choose File > Preferences > Network.
2. Double click on VirtualBox Host-Only Ethernet Adapter. Update the settings as shown and click Ok twice.
IPv4 Address: 192.168.78.1
IPv4 Network Mask: 255.255.255.0
3. Create a virtual hard drive now >
VDI (VirtualBox Disk Image)> Dynamically allocated> Location /London> size 30G
4. Disable USB
5. Allocate the minimum physical memory required ( 3.5G<Memory<4G )
o Storage: Delete the Empty disk under the IDE Controller
> Add CD/DVD Device
> Locate and open the rhel-server-7.1-x86_64- dvd.iso file.
o Network: Adapter 1: Host-only Adapter.
Adapter 2: Internal Network (Name: rac-priv) .
Adapter 3: NAT .
Shared folder 12gR2 : on shared folder link the diretory containing all the installation files and name it 12gR2
You can mount it later using the following command mount -t vboxsf 12gr2 /mnt
2. Create the first node Go to Top
1). Linux RedHat Enterprise installation :
A. Click on Start to boot the virtual machine. If asked to select a start-up disk, choose RHEL7 iso.
o Skip the CD testing by pressing the right arrow key and press enter.
o From now on you can use the mouse to navigate. To unlock the mouse and keyboard from the VM, hit the right Ctrl or
Alt key.
Click Next.
B. Under LOCALIZATION
o LANGUAGE SUPPORT : Leave/select English (English) selected .
– Adapt or leave the timezone settings as they are and exit.
o KEYBOARD : Leave U.S. English selected and exit (unless you have another preferred keyboard layout).
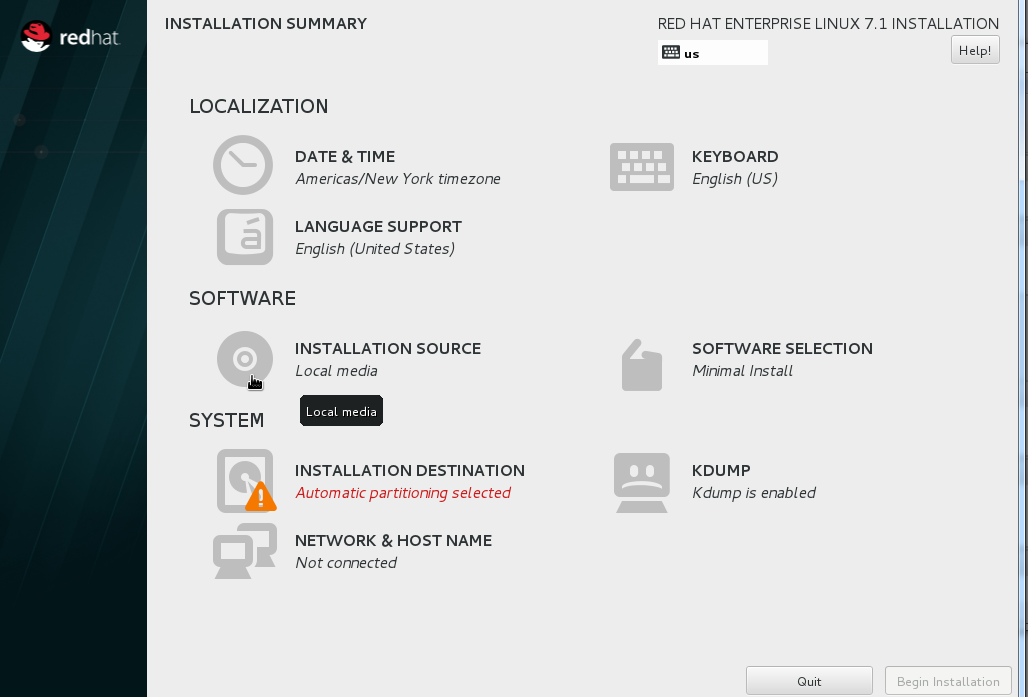
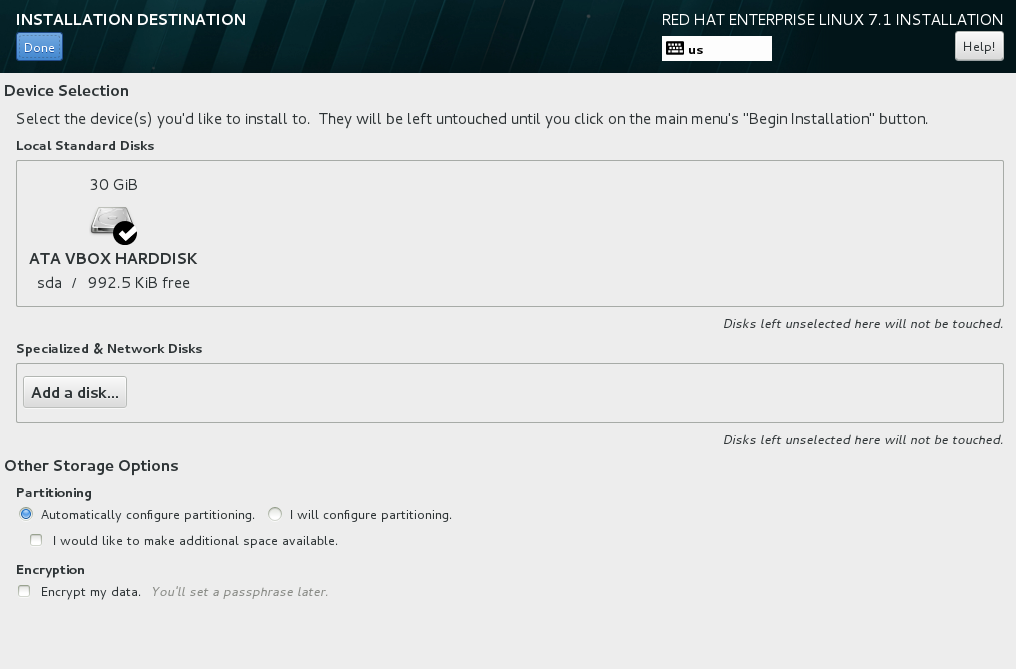
C. Under INSTALLATION DESTINATION Leave Basic Storage Devices selected and exit.
o Click Yes, discard any data for the warning box stating The storage device below may contain data.
D. Under NETWORK AND HOSTNAME
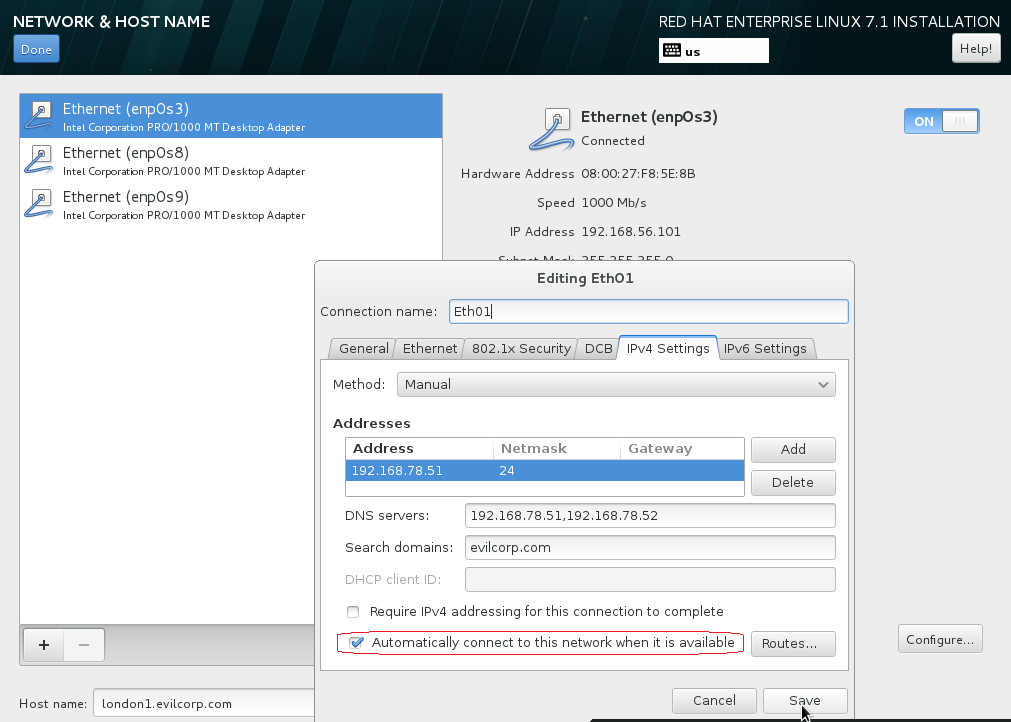
In the hostname field, type london1.evilcorp.com .
D.1 Highlight EnpOs3 interface and click the Configure… button.
- Click the IPv4 Settings tab.
Click the Connect automatically checkbox. Click the Method: dropdown and select Manual. Click Add and type 192.168.78.51 for the address. Leave Netmask at 24. In the DNS servers: box, type 192.168.78.51, 192.168.78.52. In the Search domains: box, evilcorp.com then Click the Save .
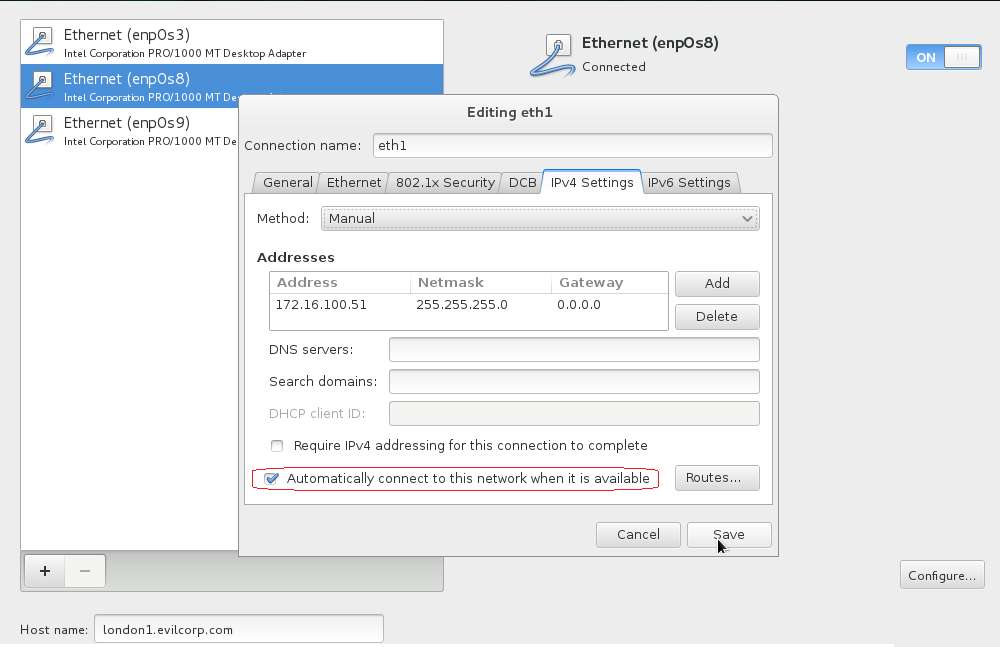
D.2 Highlight EnpOs8 Interface and click the Configure… button.
Click the IPv4 Settings tab. Click the Connect automatically checkbox. Click the Method: dropdown and select Manual. Click Add and type 172.16.100.51. Change Netmask to 24. Click the Save button.
D.3 Highlight EnpOs9 Interface and click the Configure… button.
- Click the IPv4 Settings tab.
Click the Connect automatically checkbox. Click the Method: dropdown and select Automatic (DHCP) addresses only. Click the Save button. Click Close to close the NETWORK & HOST NAME menu and click Next.
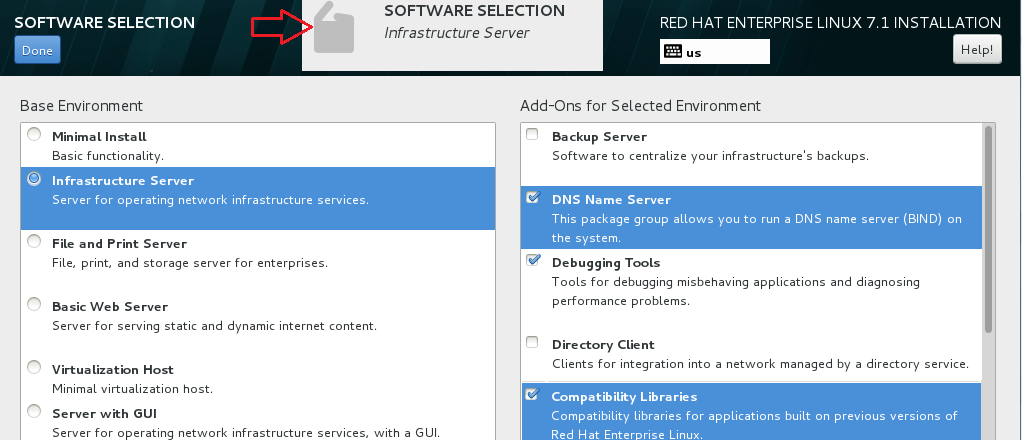
E. Under SOFTWARE SELECTION
o Choose infrastructure Server: Select DNS Name Server and Compatibility Libraries Add-Ons then exit.
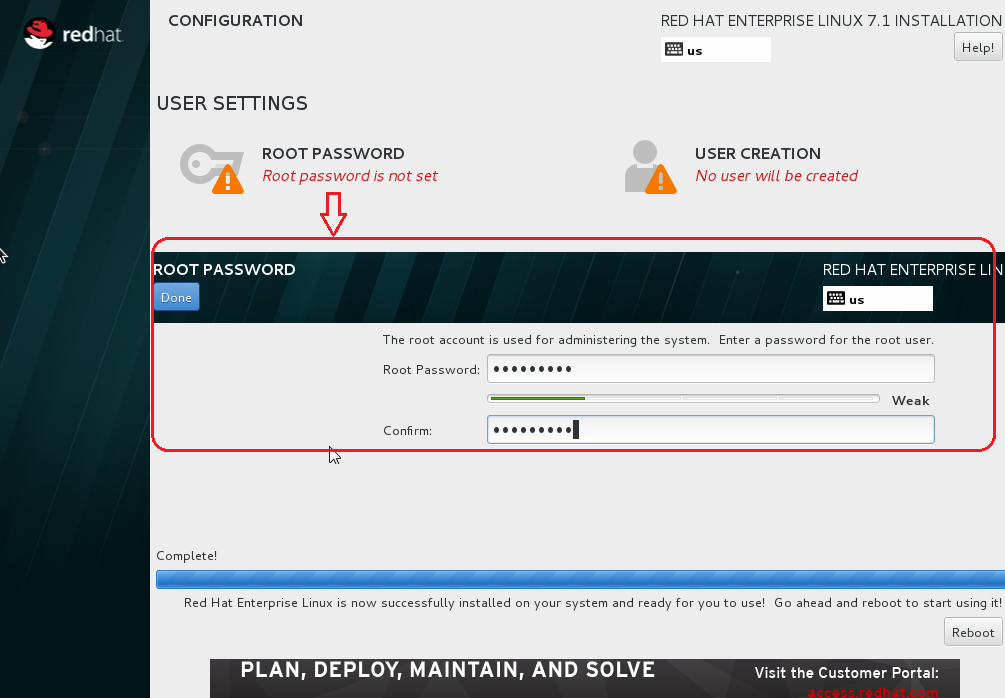
F. Complete the Installation
o Enter the Root Password as racattack (Click Use Anyway when warned about the weak password).
o Click Begin Installation
o When Installation is complete,Click Reboot.
2). Linux post installation configuration:
– We will first have to change the network interface naming from EnpOs3/8/9 to Eth0/1/2 through this *** Tutorial>>.
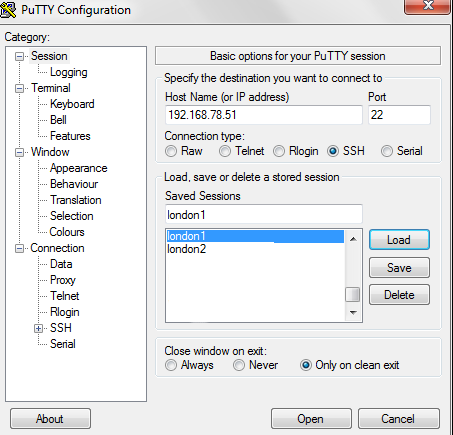
To connect to the new virtual machine, create a connection in Putty Called london1 with the IP Address of 192.168.78.51.
Optionally, create another connection for london2 with the IP Address of 192.168.78.52 that will be created later as a clone of london1.
Open the london1 connection by clicking Open.
– Enter root at the login as: prompt and racattack at the password: prompt.
– Remove special character occuring when hitting backspace on the terminal
# stty erase ^? or CTRL+H
o Verify the network configuration via network manager user interface
[root@localhost]# nmtui
o In case the hostname wasn’t set durring the installation run the following
[root@localhost]# hostnamectl set-hostname london1.evilcorp.com
o Confirm host configuration
[root@london1]# hostnamectl status
Static hostname: london1
Icon name: computer Chassis: n/a
Machine ID: dbd60b83d0d9470cbbf07397a6ab261e
Boot ID: 85bde258cf7b49458a397db3a7ae36a1
Virtualization: kvm
Operating System: Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server 7.1(Maipo)
CPE OS Name: cpe:/o:redhat:enterprise_linux:7.1:GA:server
Kernel: Linux 3.10.0-229.el7.x86_64
Architecture: x86_64
– Shared memory allocation
*New in REDHAT 7: tmpfsis a file system that keeps all files and folders in the virtual memory of the operating system.
Here are some of the known purposes of tmpfs:
|
Filesystem Purpose |
| /dev contains the special device files for all the devices. |
| /dev/shm contains shared memory allocation |
| /run used for system logs |
| /sys/fs/cgroup used for cgroups, a kernel feature to limit, police and account the resource usage of certain processes |
o Resize swap and dev/shm to 2G (shared memory allocation):
[root@london1]# ddif=/dev/zero of=/swapfile bs=1024k count=2000 —OR fallocate -l 2G /swapfile
1- Setup the swapfile
[root@london1]# mkswap /swapfile
2- It is recommended that the permissions are changed to prevent the swap being world readable.
[root@london1]# chmod 0600 /swapfile
3- To enable the swap file immediately but not at boot time [root@london1]# swapon /swapfile
o Setting & Mounting Shared Memory File System on Linux (I actually assigned 3G )
[root@london1]# mount -t tmpfs shmfs -o size=3072m /dev/shm
o To enable it at boot time, edit /etc/fstab to include the following entry:
[root@london1]# vi /etc/fstab (replace default by size clause)
[..]
tmpfs /dev/shm tmpfs size=3g 0 0
/swapfile swap swap defaults 0 0
o Check the new swap size
[root@london1]# swapon -s —- OR # cat /proc/swaps
– OS Configuration
Install Required Linux Packages for Oracle Grid Infrastructure and Oracle Database 12.1.0.2 :
Required Packages
————————————————————
binutils
libX11
compat-libcap1
libXau
compat-libstdc++-33
libaio
gcc
libaio-devel
gcc-c++
libdmx
glibc-devel
glibc
ksh
make
libgcc
sysstat
libstdc++
xorg-x11-utils
libstdc++-devel
xorg-x11-xauth
libXext
libXv
libXtst
libXi
libxcb
libXt
libXmu
libXxf86misc
libXxf86dga
LibXxf86vm
nfs-utils
o Add a local DVD repository
[root@london1]# mount /dev/cdrom /media
[root@london1]# vi /etc/yum.repos.d/rhel71.repo
[rhe64]
name=Red hat Linux 7.1 x86_64
baseurl=file:///media
gpgcheck=0
enabled=1
Add Virtual Box guest addition plugin
– Note: Due to some headers mismatch check and possible execution errors, few rpms may need to be installed first :
[root@london1]# yum install gcc gcc-c++ kernel-devel autoconf automake -y
[root@london1]# umount /media
– Make the VirtualBox guest additions available to the OS by clicking Devices>Install Guest Additions
o Run the below commands
[root@london1]# mount /dev/cdrom /media
[root@london1]# sh /media/VBoxLinuxAdditions.run
[root@london1]# umount /media
Note : Some of the Install Guide requirements will already be present from the “default-RPMs” foundation of Linux that you started with (including gcc’s installed above) . The rest is located in the DVD except the compat_libstdc++-33.
– compat-libstdc++-33-3.2.3-72.el7.x86_64 needs to be downloaded from redhat repository (30 days trial) or can be found as Oracle linux equivalent on https://yum.oracle.com/repo/OracleLinux/OL7 or rpm.pbone.net
– Make the linux RHEL7 DVD available to the OS
– Run the below commands to install the required rpms
[root@london1]# mount /dev/cdrom /media
[root@london1]# yum install binutils compat-libcap1 compat-libstdc++-33 elfutils-libelf elfutils-libelf-devel gcc gcc-++ glibc glibc-common glibc-devel glibc-headers ksh libaio libaio-devel libgcc libstdc++ libstdc++-devel make numactl-devel sysstat unixODBC unixODBC-devel libXxf86vm cpp libdmx mpfr kernel-headers xorg-x11-utils libXmu xorg-x11-xauth libXt libXv libXxf86dga nfs-utils
[root@london1]# rpm -ivh compat-libstdc++-33-3.2.3-72.el7.x86_64
o Additional rpms for other tools (i.e VNC)face
[root@london1]# yum install tigervnc-server.x86_64 xclock man parted.x86_64 unzip.x86_64 xterm lsof bind xorg-x11-twm
.. warning… No package xorg-x11-twm available
o Note: The reason behind the non-availability of xorg-x11-twm package is because it has been discontinued in RHEL 7 and replaced by metacity.
Solution : Install the below packages :
[root@london1]# yum install xorg-x11-xinit xorg-x11-font-utils xorg-x11-fonts-Type1 libX11-common xorg-x11-xauth libX11 dbus-x11 xorg-x11-server-utils xorg-x11-xkb-utils tigervnc-server xterm
o Next , just download and install xorg-x11-twm from your favorite CentOS 6 mirror
[root@london1]# rpm -ivh –nodeps xorg-x11-twm-1.0.3-5.1.el6.x86_64.rpm
o For maximum flexibility you can add the following CentOS 7 packages
[root@london1]# yum install xorg-x11-fonts-75dpi xorg-x11-fonts-100dpi xorg-x11-fonts-misc
o Finally, verify that all the rpms are installed by typing the below rpm commands
— Oracle RPMs
[root@london1]# rpm -vq cloog-ppl libXxf86misc ppl binutils compat-libcap1 compat-libstdc++-33 elfutils-libelf elfutils-libelf-devel gcc gcc-c++ glibc glibc-common glibc-devel glibc-headers ksh libaio libaio-devel libgcc libstdc++ libstdc++-devel make numactl-devel sysstat unixODBC unixODBC-devel libXxf86vm cpp libdmx mpfr kernel-headers xorg-x11-utils libXmu xorg-x11-xauth libXt libXv libXxf86dga nfs-utils
— VNC rpms
[root@london1]# rpm -vq xorg-x11-xinit xorg-x11-font-utils xorg-x11-fonts-Type1 libX11-common xorg-x11-xauth libX11 dbus-x11 xorg-x11-server-utils xorg-x11-xkb-utils tigervnc-server xterm
o System parameter change :
Here is the list of system parameters to be adapted :
Virtual Memory: Shared Memory (SHMMAX, SHMALL, SHMMNI) Semaphores (SEMMSL, SEMMNI, SEMMNS) Ephemeral Network Ports Optimizing Network Settings Setting NOZEROCONF Increasing synchronous I/O Requests Increasing File Handles Kernel Panic On OOPS Parameter Disabling the avahidaemon service (N/A)
Note: Prior to making any changes to the /etc/sysctl.conf, create a backup as follows:
[root@london1]# cp /etc/sysctl.conf /etc/sysctl.conf.bkup
o Adapt the content of sysctl.conf with the bellow lines if they are different or not present.
[root@london1]# cat /etc/sysctl.conf
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 0
net.ipv4.conf.default.rp_filter = 1
net.ipv4.conf.default.accept_source_route = 0
net.core.rmem_default = 262144
net.core.rmem_max = 4194304
net.core.wmem_default = 262144
net.core.wmem_max = 1048576
kernel.sysrq = 0
kernel.core_uses_pid = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 0
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 0
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-arptables = 0
vm.swappiness = 0
vm.dirty_background_ratio = 3
vm.dirty_ratio = 80
vm.dirty_expire_centisecs = 500
vm.dirty_writeback_centisecs = 100
kernel.msgmnb = 65536
kernel.msgmax = 65536
kernel.shmmax = 68719476736
kernel.shmmni = 4096
kernel.shmall = 4294967296
kernel.sem = 250 32000 100 128
fs.aio-max-nr = 1048576
fs.file-max = 6815744
net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 9000 65500
o For the changes to take effect immediately, run the following command
[root@london1]# sysctl -p /etc/sysctl.conf
o Set NOZEROCONF on /etc/sysconfig/network file
Modify this line to ensures that the route 169.254.0.0/16 is not added to the routing table. If the file is empty skip this stepce
NOZEROCONF=yes
o Disable SElinux
SELinux can prevent to establish a correct SSH communication between two hosts, or prevent the creation of ASM disks with the oracleasm tool.To disable SELinux, Edit the file /etc/selinux/config as follow:
[root@london1]# vi /etc/selinux/config
— Line to modify —>… SELINUX=disabled
— Reboot the machine and confirm SELINUX is disabled
[root@london1 ~]# getenforce
Disabled
o Disable the avahidaemon service if loaded:
[root@london1]# systemctl stop avahi-dnsconfd
[root@london1]# systemctl stop avahi-daemon
[root@london1]# systemctl disable avahi-dnsconfd
[root@london1]# systemctl disable avahi-daemon
o Turn off and disable the Firewall:
If the firewall option is operating, you will need to first manually disable UDP ICMP rejections
*Note: RHEL 7 introduced firewalld in replacement of iptables which makes /etc/sysconfig/iptables no longer relevant.
[root@london1]# systemctl stop firewalld — RHEL6 /etc/rc.d/init.d/iptables stop
o Turn UDP ICMP rejections off for all subsequent server reboots (which should always be turned off).
[root@london1]# systemctl disable firewalld — RHEL6 chkconfig iptables off
[root@london1]# rm ‘/etc/systemd/system/dbus-org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1.service’
[root@london1]# rm ‘/etc/systemd/system/basic.target.wants/firewalld.service’
[root@london1]# systemctl status firewalld
o Add Users and groups
[root@london1]# groupadd –gid 501 oinstall
[root@london1]# groupadd –gid 502 dba
[root@london1]# groupadd –gid 503 asmdba
[root@london1]# groupadd –gid 504 asmoper
[root@london1]# groupadd –gid 505 asmadmin
[root@london1]# groupadd –gid 506 oper
Note : vboxsf group allows access to the shared folders
[root@london1]# useradd –uid 501 –gid oinstall –groups dba,oper,asmdba,asmoper,vboxsf -d /home/oracle -s /bin/bash -c “Oracle Software Owner” oracle
[root@london1]#passwd oracle
Type : racattack
[root@london1]#useradd –uid 502 –gid oinstall –groups dba,asmadmin,asmdba,asmoper,vboxsf -d /home/grid -s /bin/bash -c “Grid Software Owner” grid
[root@london1]#passwd grid
Type : racattack
o Setting Shell Limits for the Grid and Oracle Users
[root@london1]# vi /etc/security/limits.d/99-grid-oracle-limits.conf
## add following hard soft limits
oracle soft nproc 2047
oracle hard nproc 16384
oracle soft nofile 1024
oracle hard nofile 65536
oracle soft stack 10240
oracle hard stack 32768
grid soft nproc 2047
grid hard nproc 16384
grid soft nofile 1024
grid hard nofile 65536
grid soft stack 10240
grid hard stack 32768
– Or : Alternatively,you can update the resource limits in the /etc/security/limits.conf configuration file for the Oracle installation owner by adding the following lines.
[root@london1]# vi /etc/security/limits.conf
## oracle user limits add the following
oracle soft nproc 2047
oracle hard nproc 16384
oracle soft nofile 1024
oracle hard nofile 65536
oracle soft stack 10240
oracle hard stack 32768
o As the root, create a shell script labeled oracle-grid.sh within /etc/profile.d/ to create the appropriate ulimits
for the oracle and grid user .
[root@london1]# vi /etc/profile.d/oracle-grid.sh
# Setting the appropriate ulimits for oracle and grid user
if [ $USER = “oracle” ]; then
if [ $SHELL = “/bin/ksh” ]; then
ulimit -u 16384
ulimit -n 65536
else
ulimit -u 16384 -n 65536
fi
fi
if [ $USER = “grid” ]; then
if [ $SHELL = “/bin/ksh” ]; then
ulimit -u 16384
ulimit -n 65536
else
ulimit -u 16384 -n 65536
fi
fi
o Add the following lines to the /etc/pam.d/login file to use limits, if it does not already exist.
session required /lib64/security/pam_limits.so
session required pam_limits.so
*Note : If you want to reference /lib/security as default library directory create the folder and run the following
[root@london1]# ln -s /lib64/security/* /lib/security/ .
o Add two modified .bash_profile to /home/oracle & /home/grid directories respectively
“.bash_oracle_profile” and “.bash_grid_profile”
(rename each of them to .bash_profile and assign a value to ORACLE_SID accordingly )
o Enable ssh: Run as oracle /and grid
[oracle/Grid@london1]# ssh-keygen -t rsa >ENTER >ENTER >ENTER. [oracle@london1]# cat /home/oracle/.ssh/id_rsa.pub >>/home/oracle/.ssh/authorized_keys
[grid@london1]# cat /home/grid/.ssh/id_rsa.pub >>/home/grid/.ssh/authorized_keys
o Create Grid oracle Directories
o Create Oracle inventory Directory
Create Oracle inventory Directory
[oracle/Grid@london1]# mkdir -p /u01/app/OraIventory
[oracle/Grid@london1]# chown -R grid:oinstall /u01/app/OraIventory
[root@london1]# chmod -R 775 /u01/app/OraIventory
– Create Grid Infrastrcuture Home directory and Oracle base
[root@london1]# mkdir –p /u01/grid/oracle/product/12.1.0.2/grid
[root@london1]# chown -R grid:oinstall /u01/grid
[root@london1]# chmod -R 775 /u01/grid
[root@london1]# mkdir –p /u01/app/grid —– Oracle BASE
[root@london1]# chown -R grid:oinstall /u01/app/grid [root@london1]# chmod -R 775 /u01/app/grid
– Create database Oracle Base Directory
[root@london1]# mkdir -p /u01/app/oracle [root@london1]# mkdir -p /u01/app/oracle/cfgtoollogs
– Needed to ensure dbca will be able to launch after rdbms install
[root@london1]# chmod -R 775 /u01/app/oracle/cfgtoollogs/ [root@london1]# chown -R oracle:oinstall /u01/app/oracle [root@london1]# chmod -R 775 /u01/app/oracle
– Create Oracle RDBMS Home directory [root@london1] # mkdir -p /u01/app/oracle/product/12.1.0.2/db_1 [root@london1]# chown -R oracle:oinstall /u01/app/oracle/product/12.1.0.2/ [root@london1]# chmod -R 775 /u01/app/oracle
o Setup oracle root profiles
[root@london1]# vi /etc/oratab grid:/u01/grid/oracle/product/12.1.0.2/grid:N
[root@london1]# chown oracle:dba /etc/oratab
o Add following lines to /root/.bashrc
ORAENV_ASK=NO ORACLE_SID=grid
. oraenv >/dev/null
unset ORAENV_ASK
3). RAC DNS configuration
————–Create Forward zone————–
[root@london1 ~]# touch /var/named/evilcorp.com
[root@london1 ~]# chmod 664 /var/named/evilcorp.com
[root@london1 ~]# chgrp named /var/named/evilcorp.com
[root@london1 ~]# chmod g+w /var/named/evilcorp.com.rev
————–Create Reverse zone————–
[root@london1 ~]# touch /var/named/evilcorp.com.rev
[root@london1 ~]# chmod 664 /var/named/evilcorp.com.rev
[root@london1 ~]# chgrp named /var/named/evilcorp.com.rev
[root@london1 ~]# chmod g+w /var/named/evilcorp.com.rev
[root@london1 ~]# chmod g+w /var/named
[root@london1 ~]# cp /etc/named.conf /etc/named.conf.org
o Edit named.conf : empty-zones-enable no; within options setion will allow one reverse zone for all networks
————–Configure Forward zone————–
[root@london1 ~]# sed -i -e ‘s/listen-on .*/listen-on port 53 { 192.168.78.51; };/’ -e ‘s/allow-query .*/allow-query { 192.168.78.0/24; localhost; };n allow-transfer { 192.168.78.0/24; };/’ -e ‘s/session.key”;/session.key”; n empty-zones-enable no;n/;’ -e ‘$azone “evilcorp.com” {n type master;n file “evilcorp.com”;n};nnzone “in-addr.arpa” {n type master;n file “evilcorp.com.rev”;n};’ /etc/named.conf
o Edit forward zone (evilcorp.com)
————–Forward zone————– [root@london1 ~]#
echo ‘$TTL 3H
@ IN SOA london1 hostmaster (
101 ; serial
1D ; refresh
1H ; retry
1W ; expire
3H ) ; minimum
NS london1
NS london2
localhost A 127.0.0.1
london1 A 192.168.78.51
london1-vip A 192.168.78.61
london1-priv A 172.16.100.51
london2 A 192.168.78.52
london2-vip A 192.168.78.62
london2-priv A 172.16.100.52
london-cluster-scan A 192.168.78.251
london-cluster-scan A 192.168.78.252
london-cluster-scan A 192.168.78.253′ >/var/named/evilcorp.com
o Edit reverse Zone (evilcorp.com.rev)
————–Reverse zone————– [root@london1]#echo ‘$TTL 3H
@ IN SOA london1.evilcorp.com. hostmaster.evilcorp.com(
101 ; serial
1D ; refresh
1H ; retry
1W ; expire
3H ) ; minimum
NS london1.evilcorp.com.
NS london2.evilcorp.com.
51.78.168.192 PTR london1.evilcorp.com.
61.78.168.192 PTR london1-vip.evilcorp.com.
51.100.16.172 PTR london1-priv.evilcorp.com.
52.78.168.192 PTR london2.evilcorp.com.
62.78.168.192 PTR london2-vip.evilcorp.com.
52.100.16.172 PTR london2-priv.evilcorp.com.
251.78.168.192 PTR london-cluster-scan.evilcorp.com.
252.78.168.192 PTR london-cluster-scan.evilcorp.com.
253.78.168.192 PTR london-cluster-scan.evilcorp.com.‘ > /var/named/evilcorp.com.rev
o Generate the rndc.key file. alternative to writing the rndc.conf file ( automatic rndc configuration)
[root@london1]# rndc-confgen -a -r /dev/urandom[root@london1]# chgrp named /etc/rndc.key
[root@london1]# chmod g+r /etc/rndc.key
o Restart named service and Enable at boot
[root@london1]#service named restart —–Redirecting to /bin/systemctl restart named.service
[root@london1]# chkconfig named on
*Note: Forwarding requires to add named.service simlink to run ‘systemctl enable named.service‘.
[root@london1]# ln -s ‘/usr/lib/systemd/system/named.service’ ‘/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/named.service’
o Finally check if the DNS configuration is well set
[root@london1]# vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg eth2
–verify if parameter PEERDNS is set to no to prevent the resolv.conf from being overwritten by the dhcp client:
verify zone PEERDNS=no
[root@london1]# cat /etc/resolv.conf
# Generated by NetworkManager
search evilcorp.com nameserver 192.168.78.51 nameserver 192.168.78.52
[root@london1]# named-checkzone evilcorp.com.rev /var/named/evilcorp.com.rev
// verify zone OK
[root@london1]# netstat -tulnp | grep –i 53
tcp 0 0 192.168.78.51:53 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 491/named
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:953 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 491/named udp 0 0 192.168.78.51:53 0.0.0.0:* 491/named
[root@london1 ~]# host london1
london1.evilcorp.com has address 192.168.78.51
3. Create shared ASM devices Go to Top
Create and attach vm disks
o Execute the following command to create 5 disks for ASM (+DATA diskgroup will use 3 ). Each command is in a single line.
C:> “C:Program FilesOracleVirtualBoxVBoxManage” createhd –filename “C:VMRAC lablondon1asm1.vdi” –size 4096 –format VDI –variant Fixed
C:> “C:Program FilesOracleVirtualBoxVBoxManage” createhd –filename “C:VMRAC lablondon1asm2.vdi” –size 4096 –format VDI –variant Fixed
C:> “C:Program FilesOracleVirtualBoxVBoxManage” createhd –filename “C:VMRAC lablondon1asm3.vdi” –size 4096 –format VDI –variant Fixed
C:>“C:Program FilesOracleVirtualBoxVBoxManage” createhd –filename “C:VMRAC lablondon1asm4.vdi” –size 4096 –format VDI –variant Fixed
C:>“C:Program FilesOracleVirtualBoxVBoxManage” createhd –filename “C:VMRAC lablondon1asm5.vdi” –size 4096 –format VDI –variant Fixed
0%…10%…20%…30%…40%…50%…60%…70%…80%…90%…100% Medium created. UUID: 02a719b5-decf-4c16-9513-632c81e86896
o
Execute the following command to attach the disks to the VM. Each command is
in a single line: (do it
through GUI if necessary)
C:> “C:Program FilesOracleVirtualBoxVBoxManage” storageattach london1 –storagectl “SATA” –port 1 –device 0 –type hdd –medium “C:VMRAC lablondon1asm1.vdi” –mtype shareable
C:> “C:Program FilesOracleVirtualBoxVBoxManage” storageattach london1 –storagectl “SATA” –port 2 –device 0 –type hdd –medium “C:VMRAC lablondon1asm2.vdi” –mtype shareable
C:> “C:Program FilesOracleVirtualBoxVBoxManage” storageattach london1 –storagectl “SATA” –port 3 –device 0 –type hdd –medium “C:VMRAC lablondon1asm3.vdi” –mtype shareable
C:> “C:Program FilesOracleVirtualBoxVBoxManage” storageattach london1 –storagectl “SATA” –port 4 –device 0 –type hdd –medium “C:VMRAC lablondon1asm4.vdi” –mtype shareable
C:> “C:Program FilesOracleVirtualBoxVBoxManage” storageattach london1 –storagectl “SATA” –port 5 –device 0 –type hdd –medium “C:VMRAC lablondon1asm5.vdi” –mtype shareable
o Create partition from above added disks
use fdisk command to partition the disks (as root).Repeat the steps below for all the disks ( sdb, sdc, sdd, sde,sdf).
— Repeat the same step for sdc, sdd and sde.
[root@london1 ~]# fidsk /dev/sdb
Command (m for help): n
Command action e extended / p primary partition (1-4)
p
Partition number (1-4): 1
First cylinder (1-652, default 1): <enter>
Using default value 1
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (1-xxx, default xxx): <enter>
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered!
— Final result
[root@london1 ~]# ls -l /dev/sd?1
brw-rw—- 1 root disk 8, 1 Jul 19 05:34 /dev/sda1
brw-rw—- 1 root disk 8, 17 Jul 19 05:52 /dev/sdb1
brw-rw—- 1 root disk 8, 33 Jul 19 05:53 /dev/sdc1
brw-rw—- 1 root disk 8, 49 Jul 19 05:54 /dev/sdd1
brw-rw—- 1 root disk 8, 65 Jul 19 05:54 /dev/sde1
brw-rw—- 1 root disk 8, 65 Jul 19 05:54 /dev/sdf1
o Configure the option -g for the scsi_id command to expect an UUID from the shared devices.
[root@london1]# printf “options=-gn–whitelistedn –replace-whitespace” > /etc/scsi_id.config
—– Create a symbolic link for scsi_id
ln -s ‘/usr/lib/udev/scsi_id’ ‘/sbin/scsi_id’
o Prepare the file /etc/udev/rules.d/99-oracle-asmdevices.rules by running the
following script:
[root@london1]# i=1
cmd=”/sbin/scsi_id -g -u -d”
for disk in sdb sdc sdd sde ; do
cat <<EOF >> /etc/udev/rules.d/99-oracle-asmdevices.rules KERNEL==”sd?1″, SUBSYSTEM==”block”, PROGRAM==”$cmd /dev/$parent”,
RESULT==”`$cmd /dev/$disk`”, SYMLINK+=”asm-disk$i”, OWNER=”grid”, GROUP=”dba”, MODE=”0660″
EOF
i=$(($i+1))
done
– Note: Choose carefully the owner of the asm disks here (OWNER=grid if the installation uses grid user and OWNER=oracle if installation will be done through oracle user).
The file content should look like the below:
KERNEL==”sd?1″,
SUBSYSTEM==”block”, PROGRAM==”/usr/lib/udev/scsi_id -g -u -d
/dev/$parent”, RESULT==”SATA_VBOX_HARDDISK_VBd306dbe0-df3367e3_”,
SYMLINK+=”asm-disk1″, OWNER=”grid”, GROUP=”dba”,
MODE=”0660″
o Reload the udev rules and restart udev:
[root@london1]# /sbin/partprobe /dev/sdb1 /dev/sdc1 /dev/sdd1 /dev/sde1
[root@london1]# /sbin/udevadm test /block/sdb/sdb1
[root@london1]# /sbin/udevadm test /block/sdc/sdc1
[root@london1]# /sbin/udevadm test /block/sdd/sdd1
[root@london1]# /sbin/udevadm test /block/sde/sde1
[root@london1]# /sbin/udevadm test /block/sde/sdf1
[root@london1]# /sbin/udevadm control –reload-rules
[root@london1]# /sbin/start_udev ** Not needed for RHEL
o Check the result
[root@london1 ~]# ls -l /dev/asm-*
brw-rw—- 1 grid dba 8, 17 Jul 19 07:28 /dev/asm-disk1
brw-rw—- 1 grid dba 8, 33 Jul 19 07:28 /dev/asm-disk2
brw-rw—- 1 grid dba 8, 49 Jul 19 07:28 /dev/asm-disk3
brw-rw—- 1 grid dba 8, 65 Jul 19 07:28 /dev/asm-disk4
brw-rw—- 1 grid dba 8, 65 Jul 19 07:28 /dev/asm-disk5
4. Clone the node Go to Top
Copy london1 VBOX hdrive
rename it to london2 and start a new vm
with a name london2 using existing london2.vdi.
-
Add virtual machine network configuration as -
Adapter 1 (host only).
-
Adapt2 : internal network rac-priv.
-
Adapter3 (NAT).
-
Add shared file 12rc_RAC
-
Attach 4 previous ASM disks
Second Node configuration LONDON2
o Startup london2 node and run
the network manager tool
[root@london2] nmtui in RHEL7 ———OR #system-config-network in RHEL6
o Set the following
-
eth0 public IP to 192.168.78.52 -
eth1 Private IP to 172.16.100.52
-
eth2 DHCP address only
-
Configure new device> dns configuration
-
Use london2.evilcorp.com as hostname
o Remove the udev network rules file. It will be regenerated on the next reboot
with the new MAC addresses.
[root@london2 ~]# rm -f /etc/udev/rules.d/70-persistent-net.rules
o Remove the HWADDR and UUID lines in the network adapter configuration files.
[root @london2]# sed -i -e ‘/HWADDR/d’ -e ‘/UUID/d’ /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth[0-2]
o Complete DNS setup
—— Stop the DNS service
[root@london2]# service named stop
—— Remove the actual DNS files
[root@london2]# rm -f /var/named/evilcorp.com /var/named/evilcorp.com.rev
—– Modify /etc/named.conf file
[root@london2]# sed -i -e ‘s/listen-on .*/listen-on port 53 { 192.168.78.52; };/’ -e ‘s/type master;/type slave;n masters {192.168.78.51; };/’ /etc/named.conf
— Check that the parameter PEERDNS is set to no in /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth2—- start the DNS service
[root@london2]# service named start
o Check that both DNS servers are working (master and slave) on the nodes. Make sure both nodes are up and runing
[root@london2 ~]# netstat -tulpn | grep :53 ** port 53 is the DNS listener port
[root@london2 ~]# dig @london1 london1.evilcorp.com
[root@london2 ~]# dig @london1 london2.evilcorp.com
[root@london2 ~]# dig @london1 london1-vip.evilcorp.com
[root@london2 ~]# dig @london1 london2-vip.evilcorp.com
[root@london2 ~]# dig @london1 london1-priv.evilcorp.com
[root@london2 ~]# dig @london1 london2-priv.evilcorp.com
[root@london2 ~]# dig @london1 london-cluster-scan.evilcorp.com
[root@london2 ~]# dig @london2 london1.evilcorp.com
[root@london2 ~]# dig @london2 london2.evilcorp.com
[root@london2 ~]# dig @london2 london1-vip.evilcorp.com
[root@london2 ~]# dig @london2 london2-vip.evilcorp.com
[root@london2 ~]# dig @london2 london1-priv.evilcorp.com
[root@london2 ~]# dig @london2 london2-priv.evilcorp.com
[root@london2 ~]# dig @london2 london-cluster-scan.evilcorp.co
o Confirm that the asm disk are present on node london2
[root@london2 ~]$ ls -l /dev/asm-*
o Setup the VNC Server on london1 and
unzip the installation files
[oracle@london1]$ vncserver :1
— Desktop is london1.evilcorp.com:1
o log on to london1 using vncviewer [192.168.78.51:1] and unzip the
install files
[oracle@london1]$ su oracle
[oracle@london1]$ unzip V46096-01_1of2.zip -d {/path/to/extract}
[oracle@london1]$ unzip V46096-01_2of2.zip -d {/path/to/extract}
Do the same with Oracle Database files : V46095-01_1of2.zip V46095-01_2of2.zip
o Use the following command to install
the cvuqdisk package on both nodes (this allows Cluster
Verification Utility to find the shared disks during installation)
[oracle@london1]$ rpm -Uvh grid/rpm/cvuqdisk-1.0.9-1.rpm
o Adjust the cvu_config to avoid the pdksh “missing package” pre-req failure
[oracle@london1]$ sed -i ‘s/CV_ASSUME_DISTID=OEL5/CV_ASSUME_DISTID=OEL7/’ grid/stage/cvu/cv/admin/cvu_config
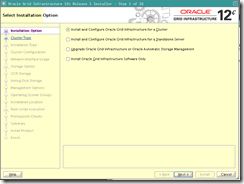
5. Install grid infrastructure 12c release 1 Go to Top
o Run Grid
Cluster installer
[oracle@london1]$ /media/sf_12cR1/grid/runInstaller
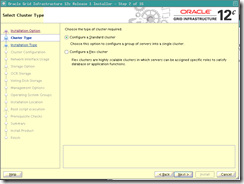
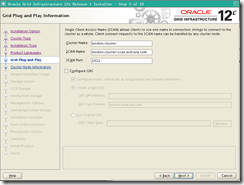
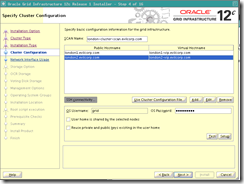
o Note : Since our SCAN Name chosen is too long (more than 15 chars.) Oracle will proposes to shorten it unless you choose advanced installation (which we are doing here).
Scan nam : london-cluster-scan.evilcorp.com cluster name : london-cluster
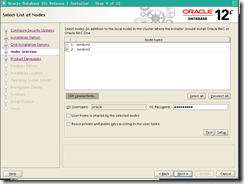
Add public hostname london2.evilcorp.com
Add virtual hostname london2-vip.evilcorp.com
SSH conectivity :
Establish passwordless ssh connectivity by typing oracle password and click setup then Ok when finished
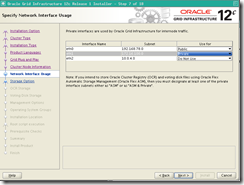
Click identify network interface : eth0 :puclic , eth1: private ,eth2: do not use
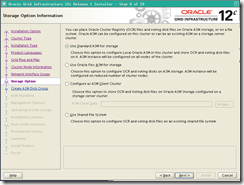
Storage Option(advanced): select standard asm for storage
Create asm disk group :
– Leave DATA as Disk Group Name.
– Select External redundancy
– If the Candidate Disks list is empty
– Click on Change Discovery Path.. Enter /dev/asm* in the Disk Discovery Path text field.
– select 3 first
disks (asm-disk1/2/3)
asm password racattack (use the same password for both asm acounts)
Failure isolation (advanced ) : Do not use IPMI (inteligent platform management interface)
Operating system group : all default dba /asmdba , asmoper
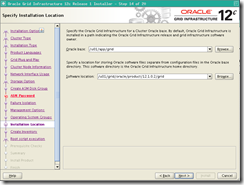
Installation location :
– ORACLE_BASE=/u01/app/grid
– GRID_HOME=/u01/oracle/product/12.1.0.2/grid
– Inventory = u01/app/OraIventory
Root script execution : Choose wether to run the rootscripts manually or allow the installer to do it automatically (with password)
Some prerequisite validation will be done at this step. It can require few minutes to complete.
– In the example above the warnings can be ignored (tick the according check box)
– Click Install
Note : you can save the installations setting into a responsefile for a future silent install
[oracle@london1]$ grid/runInstaller -silent -responseFile /home/grid/grid_rac_install.rsp -showProgress -promptForPassword // -ignorePrereq
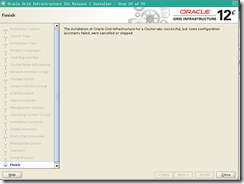
o FINAL STEP: root scripts:
execute the iguration
scripts on Both nodes as root then click ok when finished
[root@]$ /u01/app/oraInventory/orainstRoot.sh
[root@]$ /u01/app/grid/product/12.1.0.2/grid/root.sh
[root@]$ /u01/app/grid/product/12.1.0.2/grid/crs/config/rootconfig.sh
Note: In case rootconfig.sh
execution raise an error related to roothas/rootcrs perl scripts path. Adjust it as follows
[root@]$ sed -i ‘s/perl -I$ORACLE_HOME/perl/lib -I$ORACLE_HOME/crs/perl -I $ORACLE_HOME/perl/lib -I $ORACLE_HOME/crs/’ rootconfig.sh
– This will change the two following lines
ROOTHASPL=“$ORACLE_HOME/perl/bin/perl -I $ORACLE_HOME/perl/lib -I $ORACLE_HOME/crs/install $ORACLE_HOME/crs/install/roothas.pl”
ROOTCRSPL=“$ORACLE_HOME/perl/bin/perl -I $ORACLE_HOME/perl/lib -I $ORACLE_HOME/crs/install $ORACLE_HOME/crs/install/rootcrs.pl”
Post-Installation
o Execute configToolAllCommands as grid user on first node:
[root@]$ $GRID_HOME/cfgtoollogs/configToolAllCommands
6. Install the database software 12c release 1 Go to Top
o INSTALL the DBMS software
– Adjust the cvu_config to avoid the “missing package” pre-req failure command
[oracle@london1]$ sed -i ‘s/CV_ASSUME_DISTID=OEL4/CV_ASSUME_DISTID=OEL7/’ database/stage/cvu/cv/admin/cvu_config
Install database software
only then click Next
> grid install options : Oracle RAC database installation
> Node selection : make sure ssh passwordless connection works, click Next
> Instal type Entreprise , click NEXT
> Installation location
Oracle Base: /u01/app/oracle
Oracle home: /u01/app/oracle/product/12.1.0.2/db_1
> Operating system groups : Leave dba for all groups except for the OSOPER group and click Next
>…check Prereq
– In this example : one warning has a fix that I applied and the other has been ignorred during my
installation
Run /u01/app/oracle/product/12.1.0.2/db_1/root.sh as root on both nodes london1,london2 then click ok when done.
o Possible installation
failures and warnings :
Warnings :
Warning : SWAP too small+
/dev/shm not permanently mounted
Fix : make sure /dev/shm is mounted in /etc/fstab
Warning : PRVF-5056 : SCAN
listener “LISTENER_SCAN1” not running
Fix : Start the identified listener
using ”srvctl start scan_listener
Warning : Maximum locked
memory check — warning
Fix :
[root@london2-1 ~]# /tmp/CVU_12.1.0.2.0_grid/runfixup.sh
Failures :
PRVG-1561 : Setting
ORA_CRS_HOME variable is not supported
SOLUTION : $ unset
ORA_CRS_HOME
PRVF-9661 : Time offset is
greater than acceptable limit on node “london2” [actual =
“-5200.0”, acceptable = “1000.0” ]
– Cause: System
clock has drifted from the clock on the reference node for the specified set of
nodes.
– Action: If this is only generated by
CTSSD ignore
[oracle@london1]# crsctl check ctss [oracle@london2]# crsctl check ctss
CRS-4702: Offset (in msec):
0 CRS-4702: Offset (in msec): –3100
7. Create the 12c database on the cluster Go to Top
o Create +FRA asm diskgroup first
[grid@london1] oraenv
[+ASM1]
[grid@london1] sqlplus “/ as sysasm”
SQL> CREATE DISKGROUP FRA EXTERNAL REDUNDANCY DISK ‘/dev/sde1′,’/dev/sdf1’ ;
SQL> Alter diskgroup FRA mount;
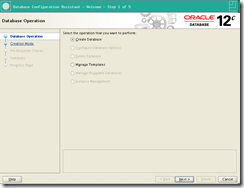
o Run the DBCA:
[oracle@london1] /u01/app/oracle/product/12.1.0.2/db_1/bin/dbca
> Select create database
> Select Create a database with default configuration.
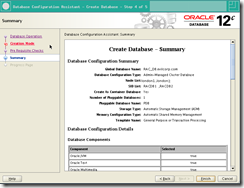
>Global Database Name: RAC_DB.evilcorp.com
Storage Type: Automatic
Storage Management (ASM)
Database Files Location:
+DATA
Fast Recovery Area: +FRA
Database Character Set:
AL32UTF8 – Unicode UTF-8 Universal character set
Administrative password:
racattack
Check Create As Container
Database
Pluggable Database Name: PDB(*)
Click NEXT
The prerequisite checks may fail due to space requirements. It’s safe to ignore by checking Ignore all. Click Next to see the summary
Click Finish to start the installation
The database creation is finished. Click Exit, then Close.
Note : Don’t forget to assign the right values to oracle_sid environment variable for both grid and oracle .bash_profile files in each nodes. (i.e ORACLE_SID=Racdb1/Racdb2 …)
o Possible installation failures and warnings
I – LONDON2 PRCR 1079 fail to start resource ora.rac_db.db
ORA-00845 Memory target not supported CLNS 00107
CRS-2674
srvctl start ora.rac_db -n london2 failed
CRS-2632 no
more servers
Cause :
The use of Automatic Memory Management
(AMM) is absolutely incompatible with
HugePages.
On
systems with HugePages in use, attempting to set the MEMORY_TARGET /
MEMORY_MAX_TARGET instance initialization parameters may result in the
mentioned error message:
ORA-00845:
MEMORY_TARGET not supported on this system
Solution (if you want to keep AMM on) :
On both nodes
1
– Add transparent_hugepage=never at the
end of the below line in the /etc/default/grub
file
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX=…
2-
Apply change on each node london1 london2
[root@]# grub2-mkconfig -o
/boot/grub2/grub.cfg
3-
Reboot the system to ensure the huge pages setting takes effect properly.
[root@]# cat /proc/cmdline
[root@]# cat /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled
[always] madvise never
II –DBCA Failing
ORA-12537: TNS: Connection closed During 12c RAC Installation
Cause : Listener (including SCAN
Listener) and Database are Owned by Different OS Users (oracle and grid)
Solution: Make sure that the file
system of the database home directory has setuid/suid set, database
binary($RDBMS_HOME/bin/oracle) has correct ownership and permission and listener owner is able to access database
oracle binary (as listener owner)
# Repeat Following on Each Node of
Cluster/Grid Infrastructure (london1, london2)
[root@london1 ~]# cd /u01/app/oracle/product/12.1.0.2/db_1/bin[root@london1 bin]# ls -l
oracle-rwxrwsr-x 1 oracle dba 323649880 Dec 22 02:53 oracle
[root@london1 bin]# chmod 6775 oracle
— first number in this command (6) means setting both setuid/suid and setgid/sgid options
[root@london1 bin]# ls -l
oracle-rwsrwsr-x 1 oracle dba 323649880 Dec 22 02:53 oracle
7. Enjoy and experiment Go to Top
We can finaly check the current status of the cluster and the RAC database resource:
[grid@london1 ~]$ crsctl stat res ora.rac_db.db -t
——————————————————————————–
Name Target State Server State details
——————————————————————————–
Cluster Resources
——————————————————————————–
ora.rac_db.db
1 ONLINE ONLINE london1 Open,STABLE
2 ONLINE ONLINE london2 Open,STABLE
——————————————————————————–
# [root@london2 bin]# srvctl status database -d Rac_DB
Instance RACDB1 is running on node london1
Instance RACDB2 is running on node london2
For a better preview of the RAC 12c features I invite you to explore it in my next post >> Enjoy and experiment