Intro
The migration journey to the cloud for a business comes in different shapes and colors. Today, we’ll explore a quick comparison between Bare metal and VM platforms, which are two IaaS compute options available in Oracle Cloud infrastructure. Although specific to OCI, you might find similar benefits and trade-offs in other Cloud platforms.
In this short post, we will revisit what the VM platform has to offer compared to the Bare Metal Option and remind where Bare Metal offerings still make sense.
Why Opt for Virtualized Platforms over Bare Metal?
At present, your organization might utilize bare metal servers to support your critical applications. While BM servers offer high performance and dedicated resources, there are several compelling advantages to migrating to VM-based machines within OCI.
Side note: Broadcom just acquired VMware and decided to split it, which brings a lot of uncertainty to its customers and partners. So you might as well consider your options.
Here’s a small list:
I. Enhanced Agility
With VM-based machines in OCI, you can dynamically scale resources up or down, ensuring optimal performance while maximizing cost-efficiency.
- High scale VM provisioning:
No need to wait for a new physical host to deploy more resources as VMs can be created by thousands with a base CPU power up to 32 core for Intel and 64 for AMD. - Elastic compute shapes:
Only in VMs can you access flex shapes (Intel/AMD) that allow for a custom number of CPUs and memory size to fit your specific application needs. Example: High memory but low CPU workloads (3 CPU | 112 GB).

-
- You can change your VMs shape without having to rebuild your instances or redeploy your applications.
Extended Memory VMs
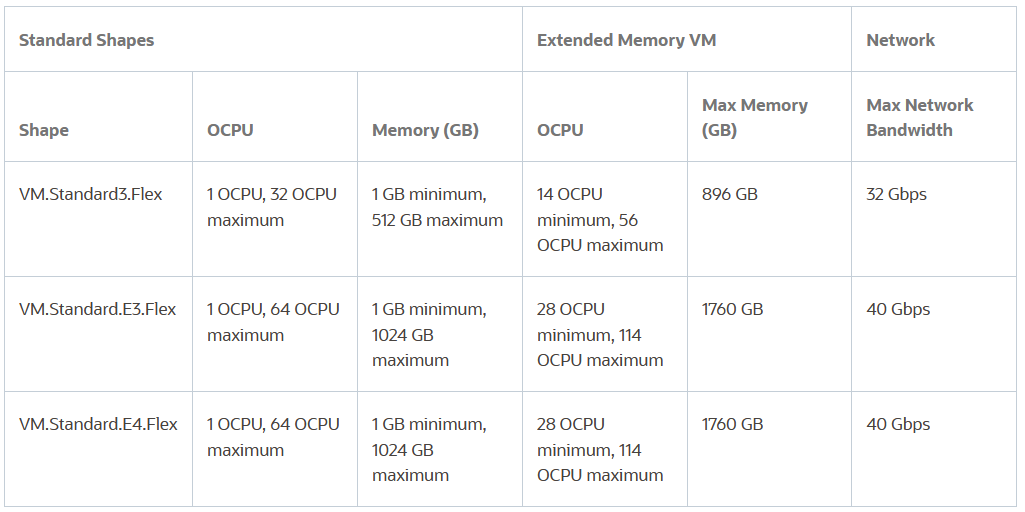
In May 2023, OCI launched Extended memory VM instances to provide more memory and CPU cores that exceed the amount a single physical socket carries (see table below).
Supported flex shapes:
VM.Standard3.Flex, VM.Standard.E3.Flex, VM.Standard.E4.Flex & VM.Standard.E5.Flex
- You can change your VMs shape without having to rebuild your instances or redeploy your applications.
How does that work?
The extended VMs are given cores and memory across multiple physical sockets. However, you should remember to optimize your application layer to be NUMA aware.
Extended AMD flex example
Extended Intel flex example

-
Block Volume Performance Auto Tuning
Enables Block Volume to adjust the volume’s performance between levels you specify, based on the actual monitored performance of a volume, like CPU auto-scaling but for storage. Learn more here.
How does that work?
- You set the min and max performance based on volume performance units per GB (VPUs/GB).
- More VPUs will allocate more resources to a volume, increasing IOPS/GB and throughput/GB.
- Block Volume adjusts the performance to the min level as much as possible.
- As volume load increases, the performance is scaled up as needed, on a best-effort basis.
- The metrics used to trigger the tuning are:
- Volume throttled operations
- Volume guaranteed VPUs/GB, IOPS, and throughput
- Scale to 0: Detached volume performance auto-tuning feature even enables adjusting the performance level to Lower Cost (0 VPUs/GB) when the volume is detached.
II. Cost Effectiveness
Turn off the light service
You can schedule the shutdown of idle servers when not needed (after hours/weekends) and stop paying for compute to save money (not possible in BM hosts that stay up even if underlying VMs are down).
Host and hypervisor overhead
Unlike on BM hosts, the physical and hypervisor layer is taken care of by Oracle Cloud, which will leave a lot more time for your Ops team to focus on application performance and enable the developers.
License Compliance Simplified
Migrating to OCI VM-based machines eliminates the need to pin cores to comply with software license agreements. Oracle provides “Intellectual Property (IP) License Assurance” for VM instances, which means you no longer have to allocate dedicated cores for specific software licenses. This allows you to optimize resource utilization and reduce costs.
Bring Your Own License (BYOL)
OCI VM-based machines offer the flexibility to leverage your existing licenses through the BYOL program. You can bring your current licenses for Oracle Database, WebLogic Server, and other Oracle products and enjoy cost savings by deploying them on VM instances in OCI. This way, you can maximize your existing investments and minimize licensing costs.
III. VM Infrastructure Added Value Services
Optimized Network Virtualization

OCI’s VM-based machines leverage a highly optimized KVM layer that takes full advantage of isolated network virtualization. The network virtualization is separated from the host and hypervisor, ensuring enhanced security and isolation for your applications and data. This architecture provides a robust and reliable foundation for your workloads.
Simplified Management and Deployment
OCI’s VM-based machines are fully integrated with Oracle’s suite of management and automation tools. This includes all API-based tooling: OCI Console, OCI CLI, and Terraform via Resource Manager.
These tools simplify provisioning, monitoring, and managing your VM instances, ensuring a seamless migration experience and easing full stack DR implementation.
Enhanced Observability:
OCI’s VM-based machines have native integration with comprehensive monitoring/observability tools through the Cloud Observability and Management Platform. This platform streamlines logging and offers specialized metrics and insights for WebLogic Server and Oracle Database.
WebLogic Server Monitoring
Native monitoring allows you to track critical metrics of your WebLogic Server instances, such as response times, throughput, JVM memory utilization, and thread pool usage. You can set up alerts based on thresholds for these metrics to ensure that you are notified when any performance degradation occurs (e.g., response times).
Database
Monitor key database performance metrics, such as CPU usage, memory utilization, I/O latency, and query execution times from OCI console, and offer proactive alerts and logging. OEM is also supported for enterprise edition licenses.
Native Security Features: Not Out of the Box in Bare Metal
OS Management Service
Allows automation of the patch management process through scheduled patching for your OCI VMs, which ensures that your VM instances are up to date with the latest OS security patches, reducing the risk of exploitation exposure.
Vulnerability Scanning and Security (VSS)
Provides comprehensive visibility into the security posture of your VM-based instances. VSS scans your instances regularly to identify and report all Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs) not protected on the VMs.
Audit Capabilities
IV. How about Isolation, Compliance for my VMs?
Dedicated Virtual Machine Host (Mixed Solution)
What if your company just can’t certify VMs in a multitenant infrastructure due to regulatory reasons, and must comply with isolation and licensing requirements for entire servers (host-based license)? Bare metal might be the solution, but you still don’t want the overhead of maintaining the hypervisor layer. OCI Dedicated VM hosts answer that very issue by allowing you to run VM instances on dedicated servers, which are single-tenant and not shared with other customers.
Advantages:
- Simplicity: the entire hypervisor layer is managed & supported by OCI (less overhead).
- Most OCI VM features supported provisioning, managing VMs via the console, API, CLI.
- A range of dedicated VM host shapes to choose from like Intel/AMD & flexible ones.
- Shapes that support flexible hosted VMs billed based on OCPUs & RAM separately
Caveats:
- You are still billed for the entire host upon creation like Bare Metal host.
- Some OCI compute VM features are not supported:
- Autoscaling, Burstable instances, Capacity reservations.
- Instance shape change, Instance Pools.
- Reboot & live migrations (use manual migration instead).
- No CPU overcommit possible and less control compared to the classic Bare Metal option.
V. BYOL Considerations in the Cloud
There are a few things worth noting regarding BYOL licensing in OCI and in the cloud in general.
Scaling and Partitioning:
- BYOL licenses don’t align with the dynamic or autoscaling compute model.
- In BM hosts, BYOL can work for Oracle products, but customers have to take care of the Partitioning Policy. See Oracle Partitioning Policy doc and KVM hard partitioning on Oracle Enterprise Linux.
OCI License Manager:
To simplify licensing management for both Oracle and 3rd-party software in OCI, Oracle has made a free License Manager service which allows you to:
- Eliminate overhead for software procurement and licensing.
- Enable easy tracking and reporting of license utilization.
- Provide proactive monitoring and notifications for licensing needs.
Flexible Shapes Recap:
Here’s a sample of flexible shapes like E series (AMD) but there’s more in the OCI flex compute shape reference.
Conclusion
This brief overview captures key aspects and trade-offs of the Virtualized platform vs. the Bare Metal option. While there’s a plethora of capabilities to explore, this blog focused on the most relevant ones. I strongly believe that, besides a few exceptions, VMs are the best IaaS option for you out there. If your organization is heavily dependent on hardware resources, a private cloud is a better place for you.


